Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamane, Yuichi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(11), p.1331 - 1344, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)The reactivity was estimated from a time profile of neutron count rate or a simulated data in a quasi-steady state after sudden change of reactivity or external neutron source strength. The estimation was based on the equation of power in subcritical quasi-steady state. The purpose of the study is to develop the method of timely reactivity estimation from complicated time profile of neutron count rate. The developed method was applied to the data simulating neutron count rate created by using one-point kinetics code, AGNES, and Poisson-distributed random noise and to the transient subcritical experiment data measured by using TRACY. The result shows that the difference of the estimated and reference value was within about 5% or less for (
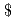
 -1) for simulated data and within about 7% or less for
-1) for simulated data and within about 7% or less for 
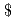
 -1.4 and -3.1 for the experimental data. It was also shown that the possibility of the reactivity estimation several ten seconds after the status change.
-1.4 and -3.1 for the experimental data. It was also shown that the possibility of the reactivity estimation several ten seconds after the status change.
Yamane, Yuichi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(8), p.926 - 931, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.16(Nuclear Science & Technology)An equation of power in subcritical quasi-steady state has been derived based on one-point kinetics equations for the purpose of utilizing it for the development of timely reactivity estimation from complicated time profile of neutron count rate. It linearly relates power,  , to a new variable
, to a new variable  , which is a function of time differential of the power. It has been confirmed by using one-point kinetics code, AGNES, that the calculated points (
, which is a function of time differential of the power. It has been confirmed by using one-point kinetics code, AGNES, that the calculated points (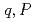 ) are perfectly in a line described by the new equation and that points (
) are perfectly in a line described by the new equation and that points (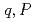 ) calculated from transient subcritical experiments by using TRACY made a line with a slope indicated by the new equation.
) calculated from transient subcritical experiments by using TRACY made a line with a slope indicated by the new equation.
Ninomiya, Hiromasa; Akiba, Masato; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Fujiwara, Masami*; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Hosogane, Nobuyuki; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Inoue, Nobuyuki; et al.
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 49, p.S428 - S432, 2006/12
To contribute DEMO and ITER, the design to modify the present JT-60U into superconducting coil machine, named National Centralized Tokamak (NCT), is being progressed under nationwide collaborations in Japan. Mission, design and strategy of this NCT program is summarized.
Ikeda, Yoshitaka; NBI Heating Group; NCT Design Team
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 49, p.S43 - S47, 2006/12
There are two type of NBI systems on JT-60U. One is the positive ion-based NBI (P-NBI) to inject the beam energy of 80-85 kV. The other is the negative ion-based NBI (N-NBI) at the beam energy more than 350 keV. Recently the pulse duration of NBI system was required to extend up to 30 sec so as to study long pulse plasmas. The four P-NBI units, which tangentially inject neutral beam to plasma, were modified to extend the pulse duration up to 30 sec with 2 MW/unit at  85 keV. The seven P-NBI units, each of which perpendicularly injects for 10 sec, were conducted to operate in series for the total pulse duration of 30 sec. The ion source of the N-NBI unit was also modified to reduce the heat load of the grid for 30 sec operation. The pulse duration was extended up to 25 sec,
85 keV. The seven P-NBI units, each of which perpendicularly injects for 10 sec, were conducted to operate in series for the total pulse duration of 30 sec. The ion source of the N-NBI unit was also modified to reduce the heat load of the grid for 30 sec operation. The pulse duration was extended up to 25 sec,  1 MW at the beam energy of 350keV. In the next step, further pulse extension of NBI up to 100 sec is planned for the modified JT-60U with superconducting coils (so called NCT). This paper reports the recent progress of the NBI system on JT-60U and the design study of the upgraded NBI system for NCT.
1 MW at the beam energy of 350keV. In the next step, further pulse extension of NBI up to 100 sec is planned for the modified JT-60U with superconducting coils (so called NCT). This paper reports the recent progress of the NBI system on JT-60U and the design study of the upgraded NBI system for NCT.
 plasma operation
plasma operationTamai, Hiroshi; Akiba, Masato; Azechi, Hiroshi*; Fujita, Takaaki; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Hashizume, Hidetoshi*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Horiike, Hiroshi*; Hosogane, Nobuyuki; Ichimura, Makoto*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 45(12), p.1676 - 1683, 2005/12
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:45.53(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Design studies are shown on the National Centralized Tokamak facility. The machine design is carried out to investigate the capability for the flexibility in aspect ratio and shape controllability for the demonstration of the high-beta steady state operation with nation-wide collaboration, in parallel with ITER towards DEMO. Two designs are proposed and assessed with respect to the physics requirements such as confinement, stability, current drive, divertor, and energetic particle confinement. The operation range in the aspect ratio and the plasma shape is widely enhanced in consistent with the sufficient divertor pumping. Evaluations of the plasma performance towards the determination of machine design are presented.
Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Oikawa, Toshihiro; Ide, Shunsuke
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 81(10), p.773 - 778, 2005/10
In steady-state tokamak fusion reactors, an efficient external current drive and a large fraction of the bootstrap current are required for non-inductive operation at low circulating power. NBI is a powerful and reliable actuator for current drive and heating. A negative ion-based NBI (N-NBI) with a high beam energy more than 350 keV has been installed in the JT-60U tokamak in order to study the NBI current drive and heating in an ITER relevant regime. This paper presents recent progress of N-NBI experiments and its system in JT-60U towards steady-state operation for ITER and tokamak fusion reactors.
Ide, Shunsuke
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 81(3), p.167 - 170, 2005/03
Non-inductive current drive (CD) by radio-frquency waves in the lower hybrid range of frequency (LHRF) is one of most powerful scheme to drive a plasma current and control the current profile of a tokamak plasma externally. This paper reviews recent achievement of CD by LHRF (LHCD) in tokamak experiments with special emphasis on steady state tokamak operation and profile control in an advanced tokamak.
Shimada, Michiya; Campbell, D.*; Stambaugh, R.*; Polevoi, A. R.*; Mukhovatov, V.*; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Costley, A. E.*; Donn , A. J. H.*; Doyle, E. J.*; Federici, G.*; et al.
, A. J. H.*; Doyle, E. J.*; Federici, G.*; et al.
Proceedings of 20th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2004) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2004/11
This paper summarises recent progress in the physics basis and its impact on the expected performance of ITER. Significant progress has been made in many outstanding issues and in the development of hybrid and steady state operation scenarios, leading to increased confidence of achieving ITER's goals. Experiments show that tailoring the current profile can improve confinement over the standard H-mode and allow an increase in beta up to the no-wall limit at safety factors  4. Extrapolation to ITER suggests that at the reduced plasma current of
4. Extrapolation to ITER suggests that at the reduced plasma current of  12MA, high Q
12MA, high Q  10 and long pulse (
10 and long pulse ( 1000 s) operation is possible with benign ELMs. Analysis of disruption scenarios has been performed based on guidelines on current quench rates and halo currents, derived from the experimental database. With conservative assumptions, estimated electromagnetic forces on the in-vessel components are below the design target values, confirming the robustness of the ITER design against disruption forces.
1000 s) operation is possible with benign ELMs. Analysis of disruption scenarios has been performed based on guidelines on current quench rates and halo currents, derived from the experimental database. With conservative assumptions, estimated electromagnetic forces on the in-vessel components are below the design target values, confirming the robustness of the ITER design against disruption forces.
Sengoku, Seio
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 80(11), p.940 - 943, 2004/11
Recent spherical tokamak (ST) experiments exhibit many advantageous results including plasma start-up without center solenoid, higher fraction of non-inductive current, formation of internal thermal-barrier as seen on conventional tokamak. In order to reflect these efforts on the design of so called "non-inductive steady-state (SS) operation scenario" and "current ramp-up scenario" of low-aspect reactor, fractions of bootstrap current and neutral-beam-driven current on VECTOR-OPT reactor are estimated. The operation with this SS scenario is shown to be feasible if the normalized beta,  n, is raised to grater than 5 typical in ST.
n, is raised to grater than 5 typical in ST.
Tamai, Hiroshi; Ishida, Shinichi; Kurita, Genichi; Shirai, Hiroshi; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Sakurai, Shinji; Matsukawa, Makoto; Sakasai, Akira
Fusion Science and Technology, 45(4), p.521 - 528, 2004/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)The 1.5D time-dependent transport analysis has been carried out to investigate steady state operation scenarios with a central current hole by off-axis current drive schemes consistent with a high bootstrap current fraction for a large superconducting tokamak JT-60SC. A steady state operation scenario with HH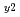 =1.4 and
=1.4 and 
 =3.7 has been obtained at I
=3.7 has been obtained at I =1.5 MA, B
=1.5 MA, B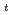 =2 T and q
=2 T and q =5 where non-inductive currents are developed during the discharge to form a current hole with beam driven currents by tangential off-axis beams in combination with bootstrap currents by additional on-axis perpendicular beams. The bootstrap fraction increases up to nearly 75% of the plasma current and the current hole region is enlarged up to about 30% of the minor radius at 35 s from the discharge initiation. The current hole is confirmed to be sustained afterward for a long duration of 60 s. The stability analysis shows that the beta limit with the conducting wall can be about
=5 where non-inductive currents are developed during the discharge to form a current hole with beam driven currents by tangential off-axis beams in combination with bootstrap currents by additional on-axis perpendicular beams. The bootstrap fraction increases up to nearly 75% of the plasma current and the current hole region is enlarged up to about 30% of the minor radius at 35 s from the discharge initiation. The current hole is confirmed to be sustained afterward for a long duration of 60 s. The stability analysis shows that the beta limit with the conducting wall can be about 
 =4.5, which is substantially above the no wall ideal MHD limit.
=4.5, which is substantially above the no wall ideal MHD limit.
Tamai, Hiroshi; Kurita, Genichi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Urata, Kazuhiro*; Sakurai, Shinji; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Morioka, Atsuhiko; Miura, Yushi; Kizu, Kaname; Kamada, Yutaka; et al.
Plasma Science and Technology, 6(3), p.2281 - 2285, 2004/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)High performance steady-state operation for JT-60SC are evaluated by the TOPICS analysis. 

 5 and bootstrap current fraction
5 and bootstrap current fraction  86% is kept steady at I
86% is kept steady at I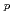 =1.5 MA, B
=1.5 MA, B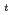 =2 T by neutral beam power of 11 MW. The ERATO-J analysis shows that the external-kink mode with multiple toroidal mode numbers of n=1 and n=2 is stable at
=2 T by neutral beam power of 11 MW. The ERATO-J analysis shows that the external-kink mode with multiple toroidal mode numbers of n=1 and n=2 is stable at 

 5.5 at the average ratio of conducting wall radius to plasma minor radius of about 1.2 with the wall stabilisation effect. Resistive wall modes, induced by a close location of the wall to plasma, is expected to be suppressed by the active feedback stabilisation with a set of non-axisymmetric field coils behind the stabilising plates. Further optimisation for the high-
5.5 at the average ratio of conducting wall radius to plasma minor radius of about 1.2 with the wall stabilisation effect. Resistive wall modes, induced by a close location of the wall to plasma, is expected to be suppressed by the active feedback stabilisation with a set of non-axisymmetric field coils behind the stabilising plates. Further optimisation for the high-
 accessibility by the plasma shaping is performed with the TOSCA analysis. The plasma shaping factor defined as S=(I
accessibility by the plasma shaping is performed with the TOSCA analysis. The plasma shaping factor defined as S=(I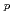 /aB
/aB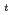 )q
)q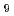
 and strongly correlated to the plasma elongation and triangularity, is scanned from
and strongly correlated to the plasma elongation and triangularity, is scanned from  4 to
4 to  6, which extends the availability of current and pressure profile control for the high performance plasma operation.
6, which extends the availability of current and pressure profile control for the high performance plasma operation.
Connor, J. W.*; Fukuda, Takeshi*; Garbet, X.*; Gormezano, C.*; Mukhovatov, V.*; Wakatani, Masahiro*; ITB Database Group; ITPA Topical Group on Transport and Internal Barrier Physics*
Nuclear Fusion, 44(4), p.R1 - R49, 2004/04
Times Cited Count:301 Percentile:76.74(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)This paper first reviews the present state of theoretical and experimental knowledge regarding the formation and characteristics of ITBs in tokamaks. Specifically, the current status of theoretical modeling of ITBs is presented; then, an international ITB database based on experimental information extracted from some nine tokamaks is described and used to draw some general conclusions concerning the necessary conditions for ITBs to appear, comparing these with the theoretical models. The experimental situation regarding the steady-state, or at least quasi-steady-state, operation of tokamaks is reviewed and finally the issues and prospects for achieving such operational modes in ITER are discussed.
Matsukawa, Makoto; JT-60 Team
IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 32(1), p.135 - 143, 2004/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:2.86(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Nakahira, Masataka
JAERI-Tech 2003-083, 79 Pages, 2003/11
The ITER Vacuum Vessel has a double-walled structure and cooling water is filled in between inner and outer shells. It is planned to apply T-welded joints with partial penetration at the connection between outer shell and rib. The length and gap of non-penetrated part are controlled and limited to less than 5mm and 0.5mm respectively. Although it can be considered to be low susceptibility, crevice corrosion can possibly occur, because the water is stagnant in the crevice and impurities will condense. In this report, the corrosion-crevice repassivation potential, E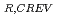 , was experimentally measured under the several density of NaCl solution, and compared to the steady-state corrosion potential in the pertinent environment, to evaluate the susceptibility. Simulated conditions are normal operating condition with water temperature of 150
, was experimentally measured under the several density of NaCl solution, and compared to the steady-state corrosion potential in the pertinent environment, to evaluate the susceptibility. Simulated conditions are normal operating condition with water temperature of 150 C, baking operation with water temperature of 200
C, baking operation with water temperature of 200 C and impurity condense by cyclic wet and dry condition.
C and impurity condense by cyclic wet and dry condition.
Kamiya, Kensaku; Kimura, Haruyuki; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Kawashima, Hisato; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Sato, Masayasu; Miura, Yukitoshi; JFT-2M Group
Nuclear Fusion, 43(10), p.1214 - 1219, 2003/10
no abstracts in English
Kamiya, Kensaku; Kimura, Haruyuki; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Kawashima, Hisato; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Sato, Masayasu; Miura, Yukitoshi; JFT-2M Group
Nuclear Fusion, 43(10), p.1214 - 1219, 2003/10
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:70.78(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Ishida, Shinichi; Abe, Katsunori*; Ando, Akira*; Cho, T.*; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Goto, Seiichi*; Hanada, Kazuaki*; Hatayama, Akiyoshi*; Hino, Tomoaki*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 43(7), p.606 - 613, 2003/07
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:69.14(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Kamiya, Kensaku; Kimura, Haruyuki; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Kawashima, Hisato; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Isei, Nobuaki; Sato, Masayasu; Shinohara, Koji
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 78(12), p.1361 - 1367, 2002/12
no abstracts in English
Nakajima, Ken; Yamamoto, Toshihiro; Miyoshi, Yoshinori
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 39(11), p.1162 - 1168, 2002/11
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:47.9(Nuclear Science & Technology)A modified quasi-steady-state method has been developed to evaluate the mean power during a nuclear excursion in fissile solution. The original method used the critical equation based on the one-group theory to calculate the reactivity. However, the one-group approximation reduces the calculation accuracy and the geometrical buckling used in the critical equation is not applicable to complex geometries. Then, we have modified the method to use the feedback coefficients of reactivity. Although the modified method requires an external calculation to obtain the feedback coefficients, it is applicable to complex geometries and gives more accurate results than the one-group approximation. Moreover, a new method to calculate the boiling power has been developed. using the experimental data of a supercritical experiment facility, SILENE. Experimental analyses were conducted to validate the new method for supercritical xperiments using CRAC and TRACY. The results showed good agreements with the experiments.
Ushigusa, Kenkichi; Ide, Shunsuke; Oikawa, Toshihiro; Suzuki, Takahiro; Kamada, Yutaka; Fujita, Takaaki; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Naito, Osamu; Matsuoka, Mamoru*; Kondoh, Takashi; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology (JT-60 Special Issue), 42(2-3), p.255 - 277, 2002/09
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:15.15(Nuclear Science & Technology)Studies on non-inductive current drive and development of an integrated steady-state high performance operation in JT-60 are reviewed. Experiments on lower hybrid current drive in JT-60 haven shown a large non-inductive current up to 3.5MA, high current drive efficiency of 3.6x1019m-2A/W. Basic studies on LH waves in JT-60 have contributed to understand current drive physics. Significant progress in neutral beam current drive has been made in JT-60 by testing the performance of negative ion based NBI (N-NBI). The CD efficiency of ~1.5x1019m-2A /W, and N-NB driven current of ~1MA have been demonstrated in N-NBCD. Strongly localized driven current by electron cyclotron current drive was identified with a fundamental O-mode scheme. Efficiency of 0.5x1019m-2A/W and EC driven current of 0.2MA were achieved and suppression of neo-classical tearing mode was demonstrated. Based on these developments, two integrated steady-state operation scenarios were developed in JT-60, which are reversed magnetic shear (R/S) plasmas and high bp ELMy H-mode. In these operation regimes, discharges have been sustained near the steady-state current profile under full non-inductive current drive. High performance plasmas with a high nDotETio and at high normalized density were also produced under fully non-inductive condition in high bp ELMy H-mode and R/S mode.